Home
Overview
This repository contributes to the development of secure, scalable, and interoperable data-sharing infrastructure. It supports NDTP’s mission to enable trusted, federated, and decentralised data-sharing across organisations.
This repository is one of several open-source components that underpin NDTP’s Integration Architecture (IA)—a framework designed to allow organisations to manage and exchange data securely while maintaining control over their own information. The IA is actively deployed and tested across multiple sectors, ensuring its adaptability and alignment with real-world needs.
For a complete overview of the Integration Architecture (IA) project, please see the Integration Architecture Documentation.
Prerequisites
- Java 21
- This repo uses a maven wrapper so no installation of maven is required.
- Docker
- Git
- Management-node
Quick Start
Follow these steps to get started quickly with this repository. For detailed installation, configuration, and deployment, refer to the relevant MD files.
1. Download and Build
To download from the github repository run the following commands:
To run a demo with multiple Federator clients and multiple Federator servers run the following commands from the project root directory:
Compile the java source code: (Replace ./mvnw with mvn to use the maven without the wrapper)
Build the docker containers:
2. Run Build Version
Run the docker containers:
You should then see the service running within docker containers. These contain multiple clients and multiple servers and their supporting services.
The service will move the data from the topic(s) in the kafka-src to federated topic(s) in kafka-target.
3. Installation
Refer to INSTALLATION.md for detailed installation steps, including required dependencies and setup configurations.
4. Uninstallation
For steps to remove this repository and its dependencies, see UNINSTALL.md.
Features
The federator enables secure data exchange between Integration Architecture nodes, supporting both server (producer) and client (consumer) roles. Key features include:
- Secure, scalable data sharing using Kafka as both source and target.
- Multiple federator servers and clients per organisation for flexible deployment.
- Filtering of Kafka messages for federation is based on the
securityLabelin the Kafka message header and the client’s credentials. The default filter performs an exact match between the client’s credentials and thesecurityLabelheader (e.g.,Security-Label:nationality=GBR). - Custom filtering logic can be configured; see Configuring a Custom Filter for details.
- Communication between federator servers and clients uses gRPC over mTLS for secure, authenticated data transfer.
- Federation currently supports RDF payloads, with extensibility hooks for other data formats on a per-topic basis.
- Integration with Management-Node for centralised configuration, topic management, and authorisation.
- Redis is used for offset tracking and short-lived configuration caching.
An overview of the Federator service architecture is shown below:
 The diagram above shows how the Federator can be used to exchange data between Integration Architecture Nodes that are running within many different organisations.
Each organisation could typically run many servers (producers) and many clients (consumers) to exchange data between their Integration Architecture Nodes.
The diagram above shows how the Federator can be used to exchange data between Integration Architecture Nodes that are running within many different organisations.
Each organisation could typically run many servers (producers) and many clients (consumers) to exchange data between their Integration Architecture Nodes.
For example within the above diagram:
- Organisation 2 (Org 2) is shown to be running two servers, with one named "Producer Node A1" that is sending messages to the topic named "DP1"
- Organisation 1 (Org 1) is shown to be running a client called "Consumer Node B2" which is reading the messages from the topic named "DP1"
It should be further noted that this diagram shows that many servers (or producers) and many clients (or consumers) can be configured within each organisation to exchange data between their Integration Architecture Nodes.
Additional note on connectivity and security: - Multiple Federator Producers and Consumers can exchange data across organisations using gRPC over mTLS. - As long as they are configured to talk to the same Management-Node, they will obtain compatible configuration (topics, roles, filters, endpoints) required for their data exchange. - The Management-Node, together with the Identity Provider, issues the certificates/credentials and tokens that enable mutual TLS and authorisation. - This means any number of Producers and Consumers can safely share data so long as their exchange requirements are defined in, and served by, the Management-Node.
Exchange data between IA nodes
The Federator is designed to allow data exchange between Integration Architecture Nodes. Kafka brokers are used as both a source of data and a target of data that is to be moved between Integration Architecture nodes. It is run in a distributed manner with multiple servers and clients.
A simplistic view of the federator service is described below:
Server (Producer)
- A server (producer) reads messages from a knowledge topic within the source Kafka broker.
- The server is configured so that it has a list of clients and the topics that they are allowed to read the messages from.
- The server also has a configurable filter that is used to decide if a message should be sent to a client.
- The server filters the messages based on the security label in the message header.
- The server streams the selected filtered messages to the client(s) using the gRPC protocol over a network.
Client (Consumer)
- A client (consumer) connects and then authenticates with its known server(s) using the gRPC protocol.
- A client requests the list of topics that it is allowed to read from the server.
- The client then requests the messages from the server for given topic(s).
- The client reads the messages and then writes them to a target Kafka broker to a topic name that is prefixed with 'federated'
The underlying communication protocol is gRPC which is used to communicate between the server and client at the network level.
Architecture
Federator Server (Producer)
This app starts the data federation server that starts a gRPC service.
This process contains the federator service supplying two RPC endpoints that are called by the client:
- Get Kafka Topics (obtain topics)
- Get kafka Consumer (consume topic)
Obtain Topics
- Is passed a user request (a client-id and key)
- Authenticate the given credentials
- Returns the topics that have been assigned to the given user.
Consume Topic
- Is passed a topic request (client-id, key, topic & offset)
- Validates the given details.
- Creates a message conductor to process the topic.
- Consumes and returns messages until stopped.
Federator Client (Consumer)
A somewhat simple app it does the following:
- Obtains topic(s) from the Server
- Checks with Redis to see what the offset is for given topic
- Obtain kafka consumer from the Server
- Process messages from consumer, adding to destination topic and update Redis offset count.
- Continue (4) until stopped. If configured, it will repeat 1-5 upon failures
Please refer to this context diagram as an overview of the federator service and its components:
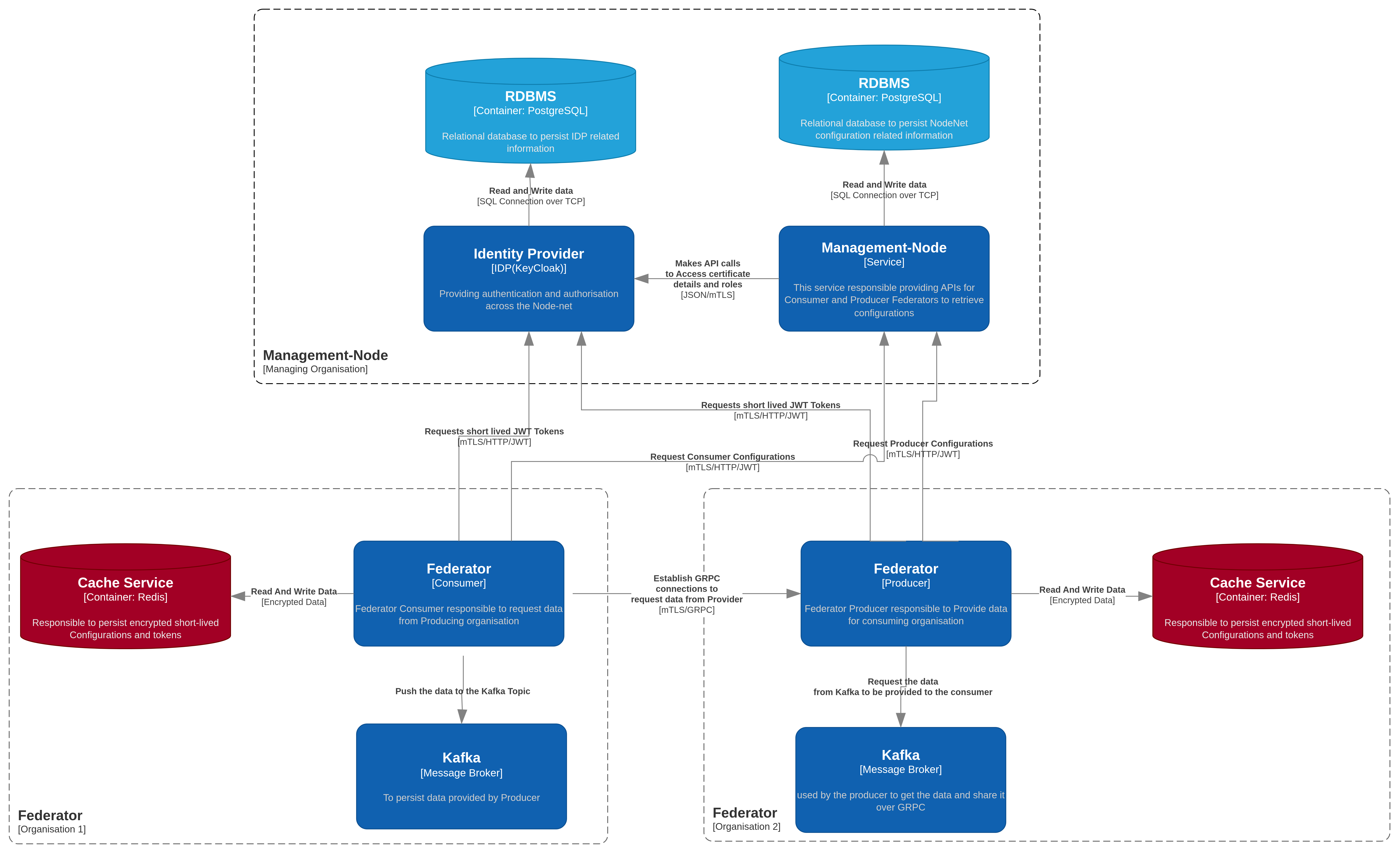
This diagram illustrates the main components involved in a typical deployment: - Federator Producer and Federator Consumer communicating over gRPC (mTLS). - Kafka clusters used by producers and consumers. - Redis cache used for short‑lived configuration and offsets/tokens. - Management-Node service that provides configuration to Federators. - Identity Provider (e.g., Keycloak) used for authentication and authorisation. - Postgres databases used by the Management-Node and Identity Provider.
See the Architecture section below for more detail on Producer and Consumer responsibilities.
Testing Guide
Running Unit Tests
Navigate to the root of the project and run mvn test to run the tests for the repository.
Public Funding Acknowledgment
This repository has been developed with public funding as part of the National Digital Twin Programme (NDTP), a UK Government initiative. NDTP, alongside its partners, has invested in this work to advance open, secure, and reusable digital twin technologies for any organisation, whether from the public or private sector, irrespective of size.
License
This repository contains both source code and documentation, which are covered by different licenses: - Code: Originally developed by Telicent UK Ltd, now maintained by National Digital Twin Programme. Licensed under the Apache License 2.0. - Documentation: Licensed under the Open Government Licence (OGL) v3.0.
By contributing to this repository, you agree that your contributions will be licenced under these terms.
See LICENSE, OGL_LICENSE, and NOTICE for details.
Security and Responsible Disclosure
We take security seriously. If you believe you have found a security vulnerability in this repository, please follow our responsible disclosure process outlined in SECURITY.
Contributing
We welcome contributions that align with the Programme’s objectives. Please read our Contributing guidelines before submitting pull requests.
Acknowledgements
This repository has benefited from collaboration with various organisations. For a list of acknowledgments, see ACKNOWLEDGMENTS.
Support and Contact
For questions or support, check our Issues or contact the NDTP team on ndtp@businessandtrade.gov.uk.
Maintained by the National Digital Twin Programme (NDTP).
© Crown Copyright 2025. This work has been developed by the National Digital Twin Programme and is legally attributed to the Department for Business and Trade (UK) as the governing entity.